Tibialis Posterior is the muscle that runs behind your shin bone and is responsible for holding up your arch and keeping your foot rolled outwards instead of 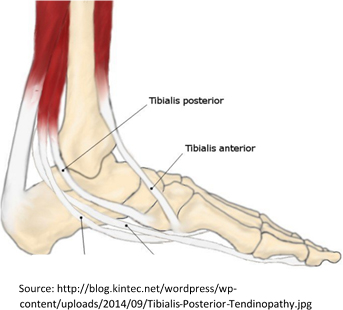 collapsing.
collapsing.
Tibialis Posterior tendinopathy is an overuse condition involving degeneration of the tendon often with some surrounding inflammation.
The overuse is usually related to a pronated (flat) foot posture and/or function. This is because in these cases the tendon has to work very hard to hold up the arch or foot as the arch is already lower and the foot already partially rolled in.
Increased levels of activity, poor footwear, weight gain or changing hormone levels (e.g. at menopause) all increase the stress felt by the tendon and increase the risk of tibialis posterior tendinopathy.
Tibialis posterior tendinopathy is felt as pain in the arch or behind your ankle on the inside of your leg. It can be achy or sharp and is worst with activity and better with rest.
It is important to treat tibialis posterior tendinopathy and to differentiate it from tibialis posterior dysfunction as dysfunction can lead to permanent changes in foot structure and painful ankle arthritis if not treated aggressively and early.
Treatment from home:
- Ice: place a frozen bag of peas on the area for 5-10 minutes at a time. Do this several times throughout the day.
- Rest from aggravating activities.
- Supportive footwear
- Doing all exercises recommended by the podiatrist to the best of your ability
Treatment from the podiatrist will be aimed at reducing the factors placing stress on the tendon. This may involve:
- Physical examination to differentiate from tibialis posterior dysfunction
- Footwear advice
- Wedging, strapping and/orshoe padding to alter the angle of your foot and support the arch area to reducing the work having to be done by the tendon.
- Orthotics to improve structure and function to reduce the work that has to be done by the posterior tibial tendon on a long term basis. This will also help prevent recurrence.
- Advice regarding exercises to do to rehabilitate and strengthen the tendon
- Return to sport advice

Comments are closed.